This post contains affiliate links, and we will be compensated if you buy after clicking on our links
Show Contents
Hide Contents
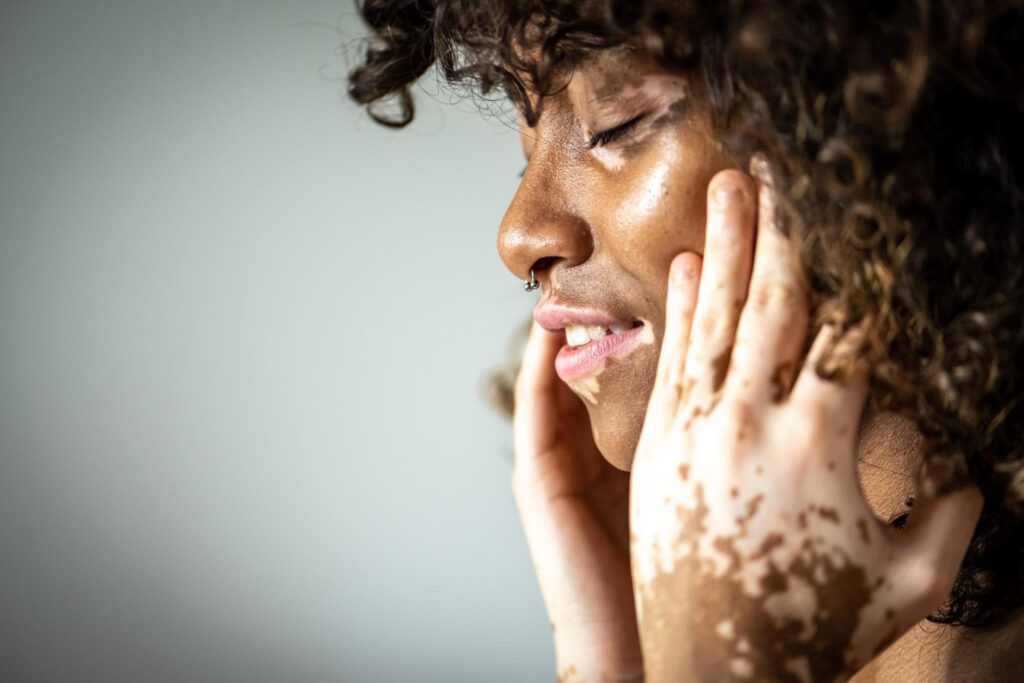 Skin Discoloration
Skin DiscolorationUnderstanding the Causes and Cures of Skin Discoloration
Skin discoloration is an increasingly common problem among people of all ages and backgrounds. This issue can manifest as dark patches, red blotches, or abnormally pale skin, causing unwanted changes in appearance that can take a toll on self-esteem.
Fortunately, it is possible to understand what causes skin discoloration and take action to remedy it. Keep reading to know more about this skin issue!
What is Skin Discoloration?
 What is Skin Discoloration?
What is Skin Discoloration?Skin discoloration is a medical condition in which areas of the skin appear darker than normal. Some factors, including sun damage, genetics, medications, and underlying health conditions, can cause it.
It can present itself in many forms, from dark patches or red, pink, and even tan blotches to abnormally pale skin, which can impact self-esteem.
What is Skin Discoloration a Sign of?
 What is Skin Discoloration a Sign of?
What is Skin Discoloration a Sign of?Skin discoloration may be an indicator of an underlying health condition. Possible causes include:
- Hormonal imbalances
- Vitamin deficiencies
- Liver or kidney problems
- Autoimmune diseases
- Medications
When these causes interfere with the body’s natural pigmentation processes, it may result in skin discoloration.
What Causes Skin Discoloration?
Birthmarks
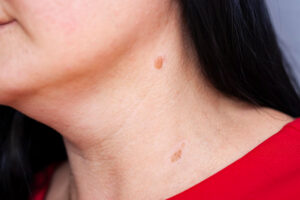 Birthmarks
BirthmarksBirthmarks are skin discoloration caused by an overgrowth of pigment cells or blood vessels. In many cases, birthmarks are harmless and do not require any special treatment.
However, some birthmarks may be associated with certain medical conditions. Therefore, getting them checked out by a doctor to rule out any potential complications is essential.
Pigmentation Disorders
 Pigmentation Disorders: Albinism
Pigmentation Disorders: AlbinismPigmentation disorders are a group of conditions that can cause patches of light or dark skin discoloration. These skin pigmentation disorders occur when there is an imbalance in the production and distribution of the skin pigment melanin. Some examples of skin pigmentation disorders are:
- Vitiligo: It causes patches of skin to lose color or pigment due to the death of melanocytes, the cells that produce melanin.
- Melasma: It’s a condition with dark patches on the face due to an overproduction of melanin in certain areas.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation: This condition occurs after inflammation or injury, such as a wound or acne breakout, and presents as darker patches of skin compared to surrounding skin.
- Albinism: This inherited condition results in a lack of pigment in the hair, eyes, and skin.
- Porphyria cutanea tarda: This condition causes red marks on the skin due to excess production of porphyrins, light-sensitive proteins in our bodies.
Medical Conditions
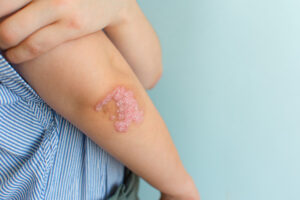 Medical Conditions: Psoriasis
Medical Conditions: PsoriasisSeveral medical conditions can also be causes of skin discoloration, including:
- Eczema: It is a condition that results in itchy, dry, and inflamed patches of skin that can lead to reddish-brown discoloration.
- Psoriasis: It is a chronic skin condition caused by the inflammation of the skin cells, which can lead to red or silvery patches on the skin.
- Dermatitis: It is similar to eczema but usually presents as an itchy, reddish rash with dry scales and bumps that may sometimes blister.
- Hives: They are another common cause of skin discoloration, which present as red or pink raised bumps on the skin caused by an allergic reaction.
Infections
 Infections: Chickenpox
Infections: ChickenpoxSkin infections, such as bacterial, fungal, and viral, can also cause skin discoloration.
- Bacterial infections, such as cellulitis, present as red, swollen, and tender areas on the skin with reddish-purple discoloration.
- Fungal infections, like ringworm, manifest with circular patches of red or silvery scales that may sometimes itch.
- Viral infections can lead to rashes with red patches caused by viruses, such as measles or chickenpox.
Allergies
 Allergies: Rashes
Allergies: RashesAllergies can cause skin discoloration or rashes, both caused by the body’s allergic response to certain substances.
Allergens like pollen, dust mites, and certain foods are the ones that you should take caution of. This can range from mild, localized areas of redness to severe hives or welts that cover large areas of the body.
In addition to symptoms like itching and swelling, some allergies may result in scaly or discolored skin patches.
Thus, it is essential to identify and avoid triggers to reduce discomfort and the risk of further skin damage.
Skin Cancer
 Skin Cancer
Skin CancerThe three most common types of skin cancer are:
- Basal cell carcinoma (BCC): Typically appears as pearly bumps on the body but can also take the form of scaly, red patches.
- Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC): Often looks similar to BCCs but may have a more crusted or scaly surface.
- Melanoma: Appears as a flat or slightly raised area of pigmentation with irregular coloration or borders.
All three forms of skin cancer can cause discoloration in various ways and should be treated by a medical professional if spotted.
Prevention
 Prevention: Use Sunscreen
Prevention: Use SunscreenHere are some ways to prevent skin discoloration:
- Use sunscreen with a minimal SPF of 30 daily.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to the sun.
- Wear protective clothing, such as caps or long-sleeved shirts, when possible.
- Eat a balanced diet of fresh fruits and vegetables that provide antioxidants and other vitamins to help protect your skin from damage.
- Drink enough water to hydrate your skin and reduce the appearance of discoloration caused by dehydration.
- Avoid harsh chemical-based skin care products, as they can irritate the skin and cause discoloration.
How is Skin Discoloration Treated?
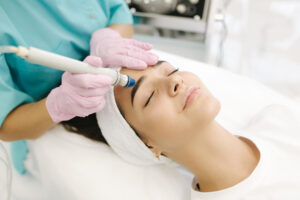 Skin Discoloration Treatment: Microdermabrasion
Skin Discoloration Treatment: MicrodermabrasionSkin discoloration can be treated with several methods, including:
- Laser treatments: Lasers can help reduce discoloration by targeting the affected skin and using heat to break up the pigments in the skin.
- Chemical peels: Chemical peels use special acids to remove the top layer of skin, which helps even out rough patches caused by discoloration.
- Microdermabrasion: This mechanical exfoliation process removes dead skin cells and increases blood flow to improve complexion and reduce discoloration.
- Prescription medications: Certain topical medications may be prescribed by a doctor to help reduce discoloration caused by melasma or other skin conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common skin discoloration types?
The most common types of skin discoloration are hyperpigmentation, age spots, melasma, vitiligo, and rosacea.
Are there any home remedies for skin discoloration?
Yes, several home remedies can help reduce skin discoloration. These include:
- Lemon juice: It can help lighten dark spots caused by hyperpigmentation due to its natural bleaching properties.
- Apple cider vinegar: This has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, which can help lighten the skin and reduce discoloration caused by acne or age spots.
- Aloe vera: It contains antioxidants that can help soothe inflammation and lighten dark spots on the skin.
- Potato juice: Potatoes contain vitamin C, which helps brighten the complexion and fade dark spots caused by sun damage or aging.
- Cucumber juice: Cucumbers also contain vitamin C, which helps even out the skin tone and reduces discoloration from sun exposure or other environmental factors.
Conclusion
All in all, skin discolorations are common skin disorders experienced by many. If you’re struggling with skin discoloration, know you’re not alone. This is a common issue that can have many causes. But luckily, there are also many effective treatments available.
You can achieve clear and healthy skin by understanding the underlying causes of your skin discoloration and working with a qualified skincare professional (if needed). In the meantime, try one of these home remedies for discoloration and see if it makes a difference. And remember: no matter what your skin looks like, you’re beautiful!
Depending on the day, you’ll find Rebecca in a well thought-out ensemble that she handcrafted herself, or in hiking and rock climbing gear. An avid outdoorswoman, cyclist, and cat lover, Rebecca reminds us all on the Groom+Style team just how much we need to get outdoors. She’s worked in spas and salons off and on before going full-time with the G+S team. Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/in/rebecca-moses-3158b914b/
View all posts